
The FIRE (Feedback In Realistic Environments) project, introduced in Hopkins et al. (2014), seeks to improve the predictive power of simulations of galaxy formation, by developing cosmological simulations that resolve the interstellar medium of individual galaxies, while implementing the major channels of stellar feedback as directly as possible from stellar evolution models, all in realistic cosmological environments. FIRE simulations typically zoom in on a region around a single primary galaxy or group of galaxies, to achieve parsec-scale resolution within a cosmological context. For more details see the FIRE homepage.
This is the main page for accessing publicly available FIRE-2 simulation data, which currently comprises 119 different simulations. These data are in HDF5 file format.
We release FIRE-2 data under the Creative Commons BY 4.0 license. If you use these data, we request that you cite as follows:
“We use the publicly-available FIRE-2 cosmological zoom-in simulations (Wetzel et al. 2023, 2025), from the Feedback In Realistic Environments (FIRE) project, generated using the Gizmo code (Hopkins 2015) and the FIRE-2 physics model (Hopkins et al. 2018)."
We also request users to cite the individual published article(s) that introduced each simulation used, as listed in Tables 1, 2, 3 in Wetzel et al. (2023) for the simulations first released in Data Release 1, or as listed in Wetzel et al. (2025) for the simulations first released in Data Release 2. See also below.
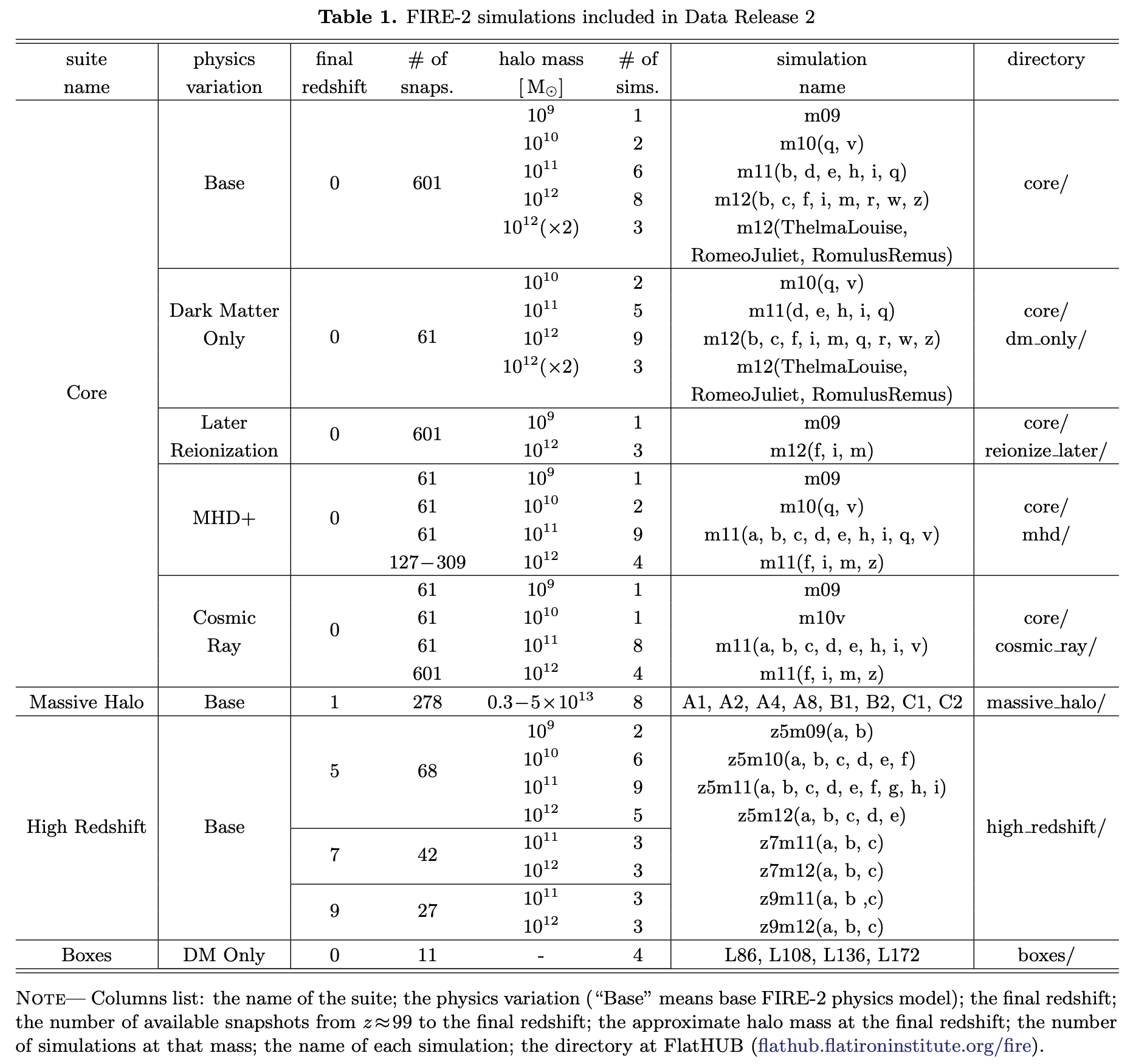
The Core suite comprises 20 simulations that zoom in on 14 Milky Way-mass galaxies, 5 SMC/LMC-mass galaxies, and 4 lower-mass galaxies, including 1 ultrafaint. For each simulation, we include all 601 snapshots across z = 0 − 99, catalogs of (sub)halos and their galaxies at all snapshots and full merger trees, and files for tracking star and gas particles across snapshots. For all star particles at z = 0, we also include a files that list their 3-D formation coordinates, and an "ex-situ" flag to indicate if they formed outside of the primary galaxy. For the Milky Way-mass galaxies, we also include catalogs of stellar streams and various representations of the gravitational potential.
The following articles introduced each of these simulations. Anyone using a given simulation also should cite that article.
For a subset of Core simulations to z = 0, we also include the following physics variations:
The Massive Halo suite comprises 8 massive galaxies: A1, A2, A4, A8 from Anglés-Alcázar et al. (2017), and B1, B2, C1, C2 from Cochrane et al. (2023), all run to z = 1. We selected these halos from the FIRE-1 MassiveFIRE suite (Feldmann et al. 2016, 2017). Each simulation includes 278 snapshots across z = 1 - 99. These halos have masses \(M_{\rm halo} = 10^{12-13.5} M_{\odot}\) at z = 1. Four simulations (A1, A2, A4, A8) include massive black hole growth, but none of these simulations include AGN feedback, which results in overly massive galaxies with ultra-dense nuclear stellar distributions at late times. Anyone using these simulations should cite Anglés-Alcázar et al. (2017) and/or Cochrane et al. (2023).
This suite comprises 34 simulations that target halos with \(M_{\rm halo} = 10^{9-12} M_{\odot}\) at z = 5 - 9, from Ma et al. (2018), Ma et al. (2019), Ma et al. (2020). All simulations start at z = 99. 22 of them are run to z = 5 (68 snapshots), 6 are run to z = 7 (42 snaphots), and 6 are run to z = 9 (27 snasphots). In addition to the primary galaxy, there are many lower-mass galaxies within each zoom-in region, so the High Redshift suite contains thousands of resolved galaxies at each snapshot. Anyone using these simulations should the Ma et al. articles above.
This suite comprises 4 dark-matter-only cosmological boxes that we used to generate zoom-in initial conditions for many (but not all) of the FIRE simulations. These boxes have comoving side lengths of 86 Mpc, 108 Mpc, 136 Mpc, and 172 Mpc, and each each one differs in mass resolution by a factor of 2. Anyone using these cosmological boxes should cite Wetzel et al. (2025).
To explore and download FIRE data, use this Globus ID, or click the "Browse" link to browse the avaiable data in your web browser.
Globus ID: d41e7ead-0fca-4715-bc72-24630cebe04b
Display Name: FIRE2 Public Release